What is the difference between cable and wire?
Understanding the distinction between cable and wire is crucial in the electrical industry. John Smith, a renowned expert in cable and wire technologies, states, "The right choice can make or break your project." This highlights the importance of understanding the term "cable and wire."
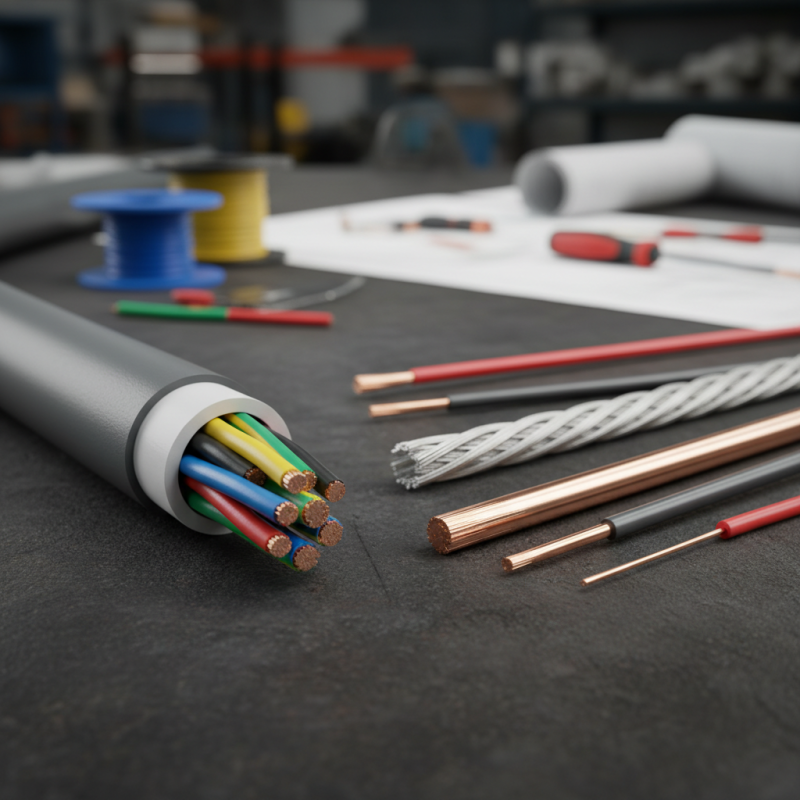
Cables and wires may appear similar at first glance, but they serve different purposes. Cables consist of multiple wires bundled together, often insulated for safety. This design offers more flexibility and protection. In contrast, a wire is a single conductor, usually made of copper or aluminum, and is simpler in structure.
Exploring the practical applications reveals their differences further. For instance, cables are common in power distribution and communication systems. Wires are often used in smaller electrical circuits. However, both are essential in modern society. Misunderstanding can lead to ineffective installations or even safety hazards. Hence, knowing when to use cable versus wire is a critical skill in the field.

Definition of Wire and Cable
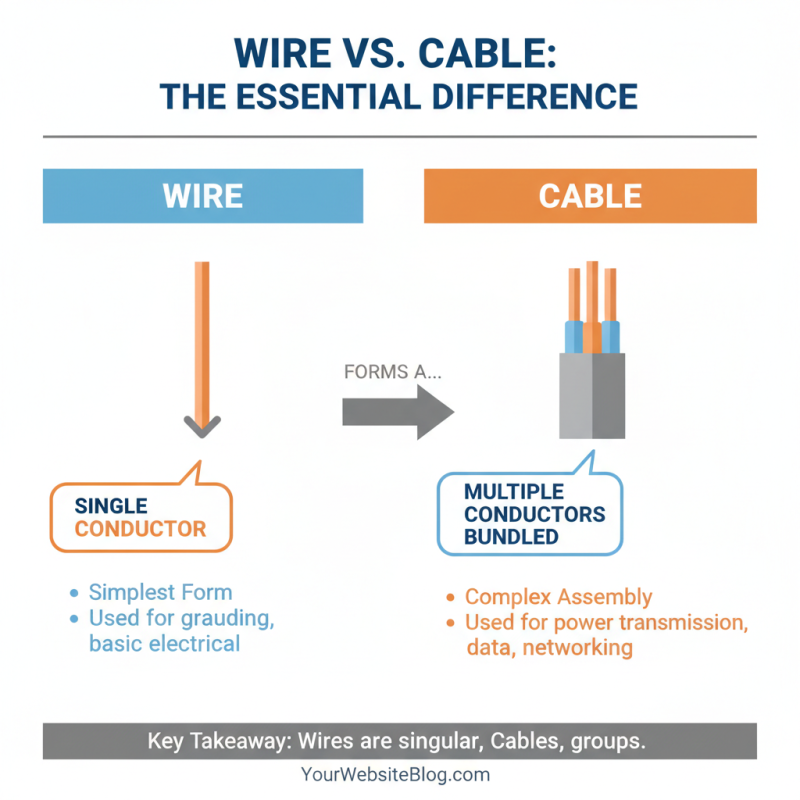
Wire and cable serve distinct purposes in electrical systems. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right materials for projects. Wire typically consists of a single conductor, while cable includes multiple conductors bundled together. This fundamental distinction impacts their applications and installations.
According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), insulated wire is often used for household wiring. It efficiently conducts electricity but can only carry limited loads. In contrast, multi-conductor cables can support more complex connections, especially in commercial environments. Reports indicate that the global demand for electrical cables is projected to grow at a rate of over 5% annually, highlighting their increasing importance.
Factors to consider include insulation type and conductor material. For instance, copper wires have excellent conductivity but can be costly. Aluminum wires are lighter but may not perform as well in some situations. As technology advances, new materials and compositions are being explored. Adaptability remains key in a rapidly changing market, challenging manufacturers to innovate while addressing quality issues. Reflecting on these distinctions helps ensure proper voltage management and general safety in electrical installations.
Components and Construction Differences
When examining cable and wire, the construction details reveal clear distinctions. Wire is a single conductor, typically made of metal. It has a simple structure and is often used for basic electrical connections. Copper and aluminum are common materials for wires. Their conductivity and flexibility are critical attributes. You often find wire in household appliances and electronic devices.
Cables, on the other hand, consist of multiple wires bundled together. They might also have additional layers for insulation and protection. This multi-layer approach enhances durability. Cables can carry larger amounts of electricity, making them essential for heavy-duty applications. The design of cables enables better resistance to environmental factors. For example, shielded cables can minimize interference from outside signals.
Understanding these nuances is essential for selecting the right electrical solution. However, many people confuse the terms, which can lead to mistakes. Using incorrect components can result in malfunctions or unsafe conditions. It's crucial to learn the differences actively. Proper knowledge reduces risks and improves efficiency in electrical projects.
What is the difference between cable and wire? - Components and Construction Differences
| Aspect | Wire | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single conductor used to conduct electricity | Multiple conductors encased in an insulating sheath |
| Construction | Typically has a single metal core | Comprises several insulated wires bundled together |
| Usage | Used for electrical connections | Used for various electronic applications including power and data transmission |
| Insulation | May or may not have insulation | Always insulated for protection |
| Flexibility | More rigid due to single composition | More flexible as it consists of multiple wires |
| Common Applications | Electrical panels, light fixtures | Telecommunication, power supply systems |
Common Applications of Wire vs. Cable
When considering wire versus cable, the applications differ significantly.
Wire generally consists of a single conductor.
It is often used in simple circuits. For example, building wiring commonly employs single-strand wire.
This type of wire is suitable for basic electrical tasks. However, exposed wires can pose risks.
They may lead to shorts or shocks if not handled properly.
Cables, in contrast, contain multiple conductors. They are usually insulated and bundled together.
This design provides better protection. Cables are ideal for complex electrical systems.
For instance, in telecommunications, cables transmit data over long distances effectively.
They also reduce interference. The flexibility and durability of cables make them essential for outdoor applications.
Nevertheless, cables can be bulkier than wires. This can make installation challenging in tight spaces.
Consider using wires for light fixtures and fans.
Cables are better for heavy-duty appliances and outdoor projects. Each application has unique needs. The choice ultimately depends on project specifications.
Be mindful of the environment. Optimal usage reduces risks and enhances performance.
Electrical Specifications and Performance
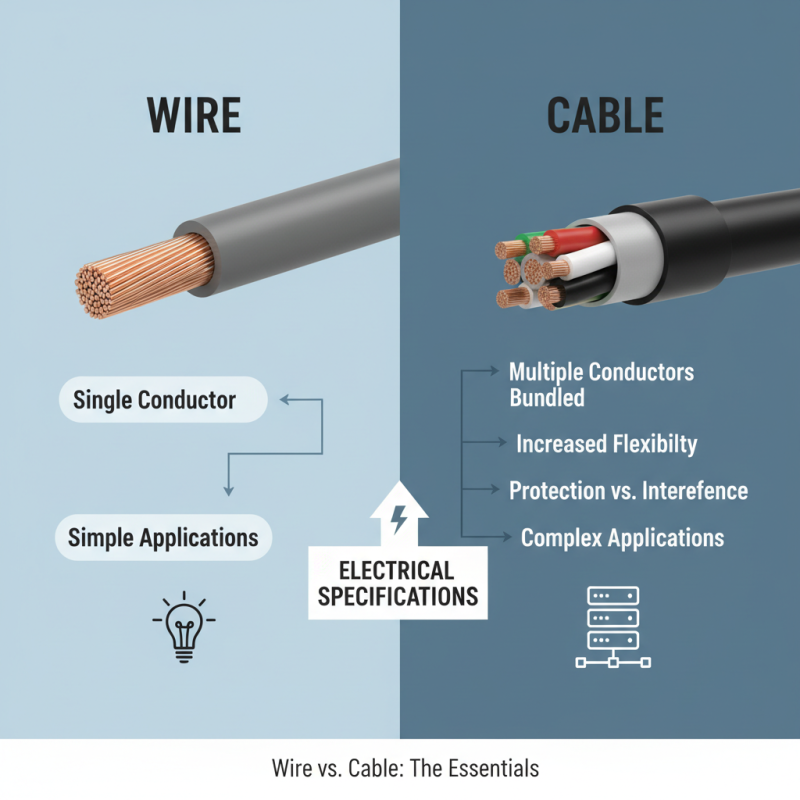
When comparing cable and wire, electrical specifications play a crucial role in their use. A wire is simply a single conductor, while a cable contains multiple wires bundled together. This design provides greater flexibility and protection against interference. Cables can handle more complex applications, making them essential for modern electrical systems.
Performance is another important aspect. Wires generally have a higher ampacity. However, cables can distribute electrical loads more evenly. This is especially vital in extensive networks. Additionally, cables are often insulated, preventing short circuits and ensuring safety. Yet, this insulation can also add bulk and weight, making installation tricky in tight spaces.
Choosing the right option depends on specific needs. Sometimes, using a wire may seem adequate. But, overlooking cable benefits can lead to performance issues. There might be cases where cables may not fit appropriately, causing frustration during installation. Ultimately, understanding both options’ specifications is essential for effective electrical design and safety.
Safety Standards and Regulations for Wire and Cable
When discussing wire and cable, safety standards play an essential role. Different applications require specific types of wiring. Many organizations set regulations to ensure user safety. These standards help prevent electrical hazards. Compliance is crucial for manufacturers and installers.
Wire is generally single conductors, while cables bundle multiple wires. This difference affects their safety ratings. Wires might not be suitable for high-tension applications. Cables often include additional insulation, offering better protection. Yet, some cables still face scrutiny over compliance. Inconsistent practices exist among manufacturers.
Awareness is key for consumers and professionals alike. Choosing the right type can mitigate risks. Improper installations often lead to dangerous situations. Regular inspections help identify potential issues. Understanding safety standards is not always easy. Many documents can be technical and dense. Engaging experts may add clarity and guide effective usage. Ensuring safety is a shared responsibility.
Related Posts
-

Maximizing Efficiency: How Electric Cable Ducts Improve Cable Management and Reduce Risks in Modern Infrastructure
-

2026 Top Cable Wire Types and Their Best Applications?
-

Understanding the Importance of Duct Cable in Modern Communication Systems
-
2025 Top Trends in Cable Baskets: Essential Guide for Organizing Wires
-
How to Choose the Right Electric Wire for Your Project?
-
Top Tips for Effective Wire Management Solutions?

